Though not yet on grocery shelves, lab-grown meat is focus of new laws and legislation

In summer 2023, the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Food Safety and Inspection Service authorized the sale of cell-cultured chicken produced by two California startups. It marked the first-ever approval by the federal agency. Later that year, for a brief period, this lab-grown meat was part of the menu at two U.S. restaurants.
Derived from the muscle tissue cells of a live animal, cell-cultured meat is grown in laboratories. Currently, cell-cultured meat is not being produced for consumption or sale in the United States.
However, continued advances in cell-cultured meat production have provoked action by several state legislatures. Perhaps most notably, in 2024, Florida and Alabama became the first U.S. states with statutory bans on the sale and production of cell-cultured meat. Soon after passage of the Florida measure, a California startup (UPSIDE) brought a case challenging the law’s constitutionality.
No such blanket prohibitions exist in the Midwest. However, new laws, as well as one gubernatorial executive order, have added new labeling requirements (Iowa, Kansas, North Dakota and South Dakota) and/or restrictions on state or local purchasing of lab-grown meat (Iowa and Nebraska).
Illinois stands apart from this regional trend. In 2023, legislators there established the Alternative Protein Innovation Task Force to explore the expansion of alternative protein sources as a way of ensuring food access, easing environmental effects and supporting the state’s economy.
Read the full Stateline Midwest article
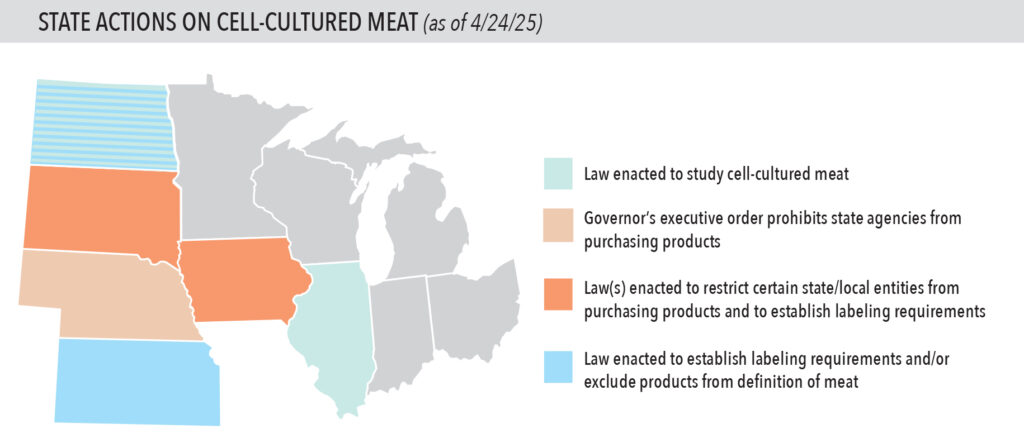
Snapshot of varying approaches taken in Midwest
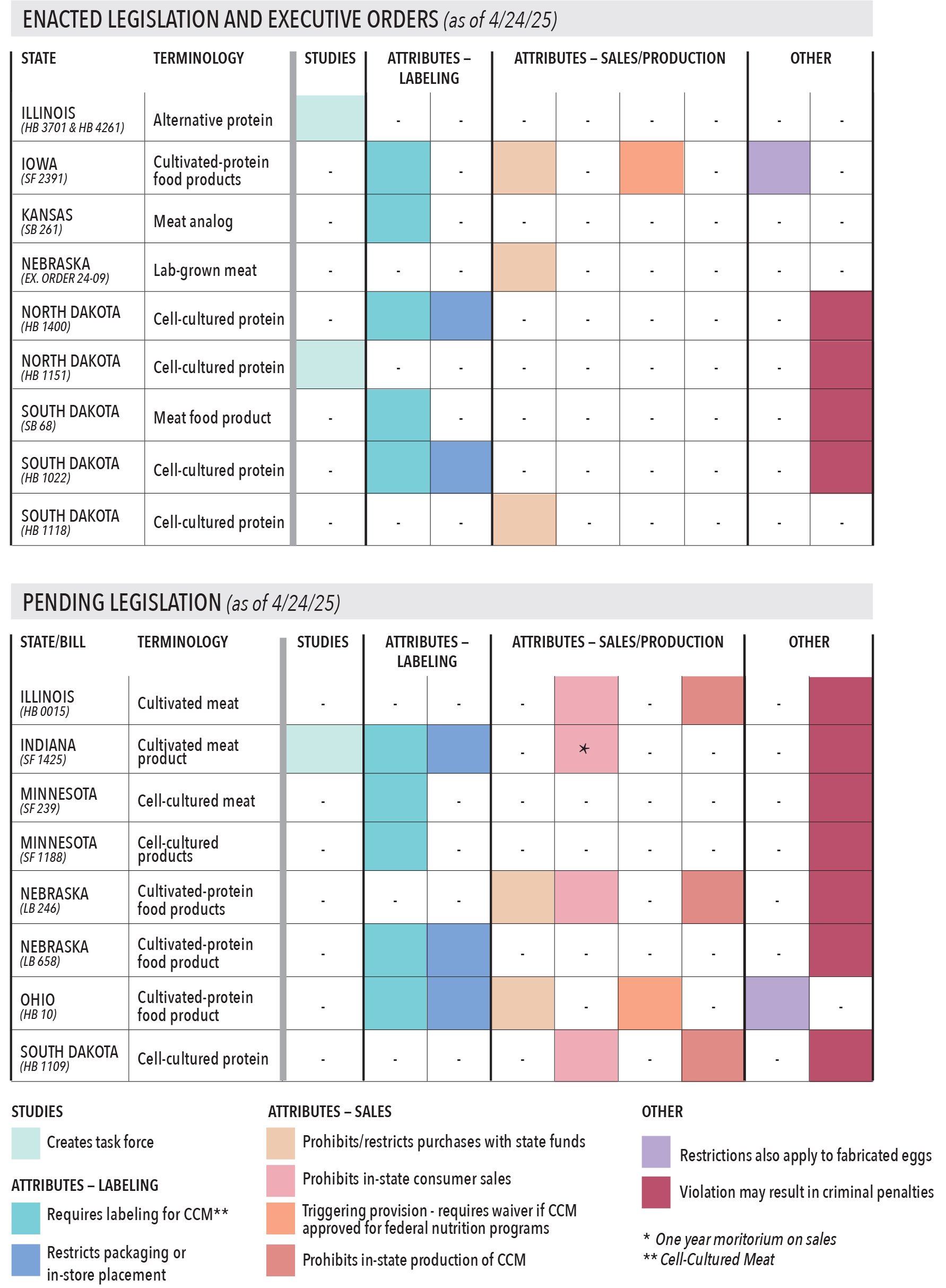
Enacted laws in Midwest: Details and links
| State | Bill Number | Description | Enacted |
|---|---|---|---|
| Illinois | HB 3701 and HB 4261 | Creates an Alternative Protein Innovation Task Force Act to explore the potential of protein derived from plant-based, fermented, or cell-cultured sources and to assess the economic, environmental, health, and food security impacts of the alternative protein industry and recommend state support strategies. | 8/11/2023 and 8/9/2024 |
| Iowa | SF 2391 | Establishes strict labeling requirements for alternative protein food products, prohibits their misbranding as traditional meat or egg products, and enforces these rules through inspections, penalties, and purchasing restrictions by state institutions. | 5/23/2024 |
| Kansas | SB 261 | Prohibits the use of identifiable meat terms on labels of meat analogs unless terms are properly qualifyed. The law specifies conditions under which food is deemed misbranded. | 7/1/2022 |
| Nebraska | Ex. Order 24-09 | Prohibits state agencies from purchasing lab-grown meat and delineating that state contractors shall not discriminate against natural-meat producers in favor of laboratory or cultivated meat producers. | 9/1/2024 |
| North Dakota | HB 1400 | Restricts labeling and product packaging of cell cultured proteins. Creates penalties for violations. | 3/12/2019 |
| North Dakota | HB 1151 | An act requiring a legislative management study regarding regulation of cell-cultured protein and litigation of state prohibitions at the state and federal level. | 4/24/2025 |
| South Dakota | SB 68 | Expands definition of misbranding food to include falsely, deceptively, or misleading labeling a product as a meat food product. | 3/29/2019 |
| South Dakota | HB 1118 | Prohibits state funds used for research, production, promotion, sale or distribution of cell-cultured protein. | 2/27/2025 |
| South Dakota | HB 1022 | Mandates clear labeling of cell-cultured protein products to prevent misbranding and ensure consumer transparency. | 2/11/2025 |
Midwest meat production: By the numbers
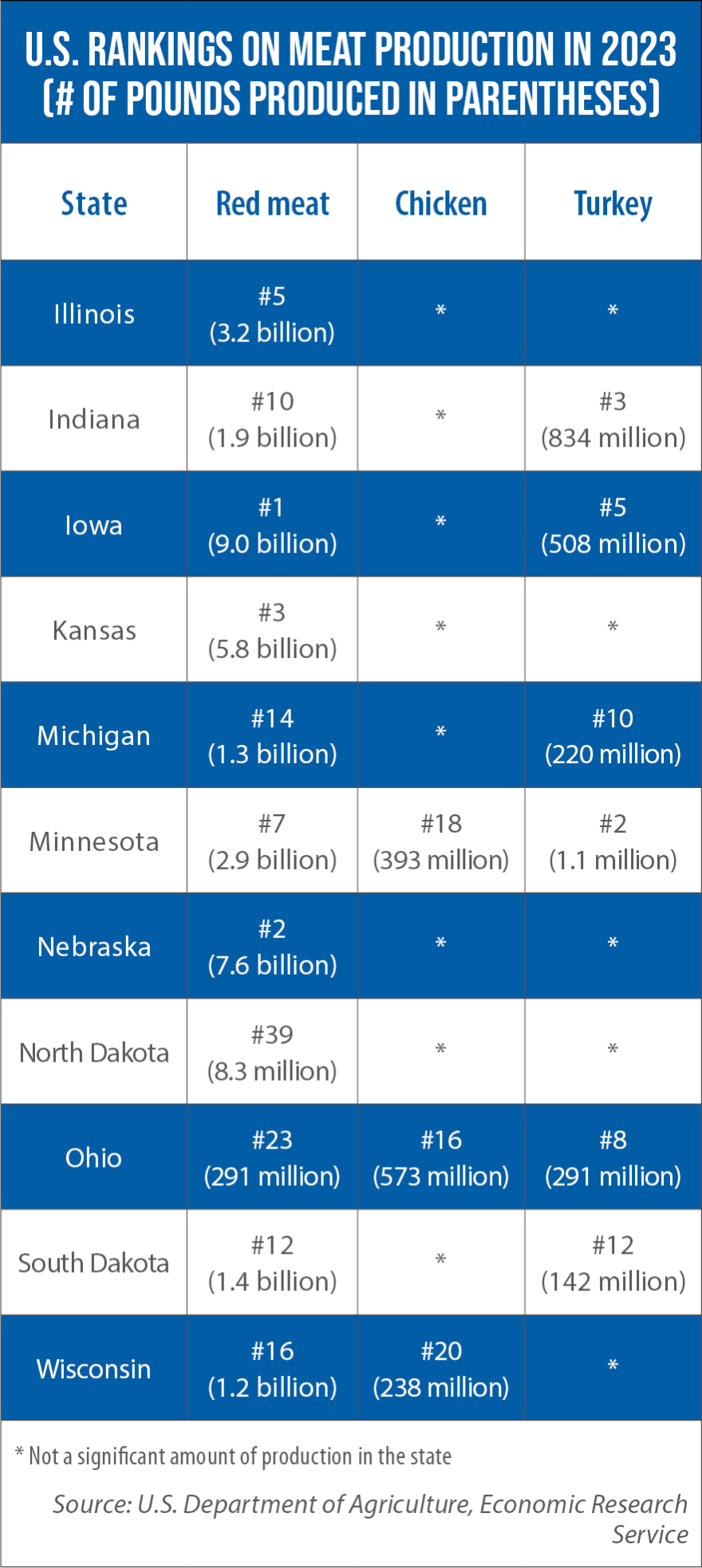 The United Nations’ Food and Agriculture Organization estimates that by 2032, global consumption of meat proteins will be 13 percent higher compared to levels at the beginning of this decade. That is significant for the 11-state Midwest region, which boasts 39.4% of total U.S. cash receipts for animal and animal product commodities. This table identifies the amount of meat production and U.S. ranking for the 11-state region.
The United Nations’ Food and Agriculture Organization estimates that by 2032, global consumption of meat proteins will be 13 percent higher compared to levels at the beginning of this decade. That is significant for the 11-state Midwest region, which boasts 39.4% of total U.S. cash receipts for animal and animal product commodities. This table identifies the amount of meat production and U.S. ranking for the 11-state region.
Cell-cultured meat: The production process
Cell-cultured meat is a product derived from animal muscle tissue that is scaled up in the lab by using a combination of growth factors, adherent cells and nutrients to form a tissue that resembles meat, according to Josephine Wee, a professor of food science at Penn State University who researches the product.
For further details about the production of cell-cultured meat, here is a link to a podcast interview with Dr. Wee.
Overview of legislative activity in 2025
In 2025, bills have been introduced in Illinois, Nebraska, North Dakota, Ohio and South Dakota to prohibit in-state production and sales of cell-cultured meat, while proposed legislation in Indiana and Minnesota focuses on labeling restrictions. South Dakota’s HB 1022, which adds labeling requirements, and HB 1118, which prohibits state funding for research, production, promotion, sale or distribution of cell-cultured protein, were signed into law in February.
North Dakota HB 1151 changed significantly prior to being signed into law in April 2025. The measure initially prohibited in-state consumer sales and production of cell-cultured protein. The enacted legislation requires a study of the regulatory landscape of implementing a prohibition of cell-cultured protein.
| State | Bill Number | Description (last updated 4/25/2025) | Primary Sponsor(s) | Date Introduced | Last Action | Last Action Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Illinois | HB 0015 | Creates the Illinois Cultivated Meat Act prohibiting the manufacture, sale and distribution of cultivated meat. Defines violations as a Class C misdemeanor and establishes enforcement by the Department of Agriculture. | Rep. Chris Miller | 1/9/2025 | Referred to Committee | 1/9/2025 |
| Minnesota | SF 239 | Defines cell-cultured meat and poultry terms and provides parameters for labeling such products in stores and at restaurants. | Sen. Rich Draheim | 1/16/2025 | Referred to committee | 1/16/2025 |
| Minnesota | SF 1188 | Defines cell-cultured products and requires a label for such products sold in stores or restuarants. | Sen. Torrey Westrom | 2/10/2025 | Referred to committee | 2/10/2025 |
| Ohio | HB 10 | Prohibits schools and institutions of higher education from purchasing cultivated-proteing food products. Requires opt-out provision if product is approved for purchase by the USDA for benefit recipients. Creates labeling and packaging requirements and civil penalties for violations. Restraints also apply to fabricated eggs. | Rep. Roy Klopfenstein and Rep. Jack Daniels | 1/23/2025 | Referred to committee | 1/28/2025 |
| South Dakota | HB 1022 | Mandates clear labeling of cell-cultured protein products to prevent misbranding and ensure consumer transparency. | House Agriculture Committee | 1/14/2025 | Signed by Governor | 2/11/2025 |
| South Dakota | HB 1109 | Prohibits in-state sale, distribution and manufacureing of cell-cultured meat for a 10-year period. | Rep. John Sjaard and Rep. Jana Hunt | 1/28/2025 | Failed Senate vote | 2/20/2025 |
| Nebraska | LB 246 | Amends the Nebraska Pure Food Act to prohibit cultivated-protein food products by classifying them as adulterated, thus making their manufacture and sale a deceptive trade practice. | Sen. Barry DeKay | 1/14/2025 | Final Reading | 4/23/2025 |
| Nebraska | LB 658 | Amends the Nebraska Pure Food Act establishing labeling and advertising requirements for food products that resemble meat but are derived from non-animal sources, such as cultivated, insect, or plant proteins. Products must be stored separately from actual meat products in food establishments. | Sen. Bob Anderson | 1/22/2025 | Amendment filed | 3/14/2025 |
| South Dakota | HB 1118 | Prohibits state funds used for research, production, promotion, sale or distribution of cell-cultured protein. | Rep. Jana Hunt Rep. Aaron Aylward | 1/29/2025 | Signed by Governor | 2/27/2025 |
| North Dakota | HB 1151 | An act requiring a legislative management study regarding regulation of cell-cultured protein and litigation of state prohibitions at the state and federal level. | Rep. Mike Schatz Rep. Ty Dressler | 1/7/2025 | Signed by Governor | 4/24/2025 |
| Indiana | HB 1425 | Requires study by state agencies regarding health and safety of cultivated meat products for human consumption. Establishes a one-year moratorium on the sale of cultivated meat products. Establishes regulations to prevent the misbranding of cultivated meat products as traditional meat, requiring clear labeling and authorizing penalties for violations. | Rep. Beau Baird | 1/13/2025 | Passed House and Senate, sent to Governor | 4/24/2025 |